JEB Decompiler for Ethereum


Use JEB to reverse engineer closed-source EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) smart contracts and dApps.
Cut down on costly reverse engineering time: decompile Ethereum smart contracts to
Solidity-like source code to easily understand and review closed-source contracts and dApps.
- Decompile EVM contract code to Solidity-like high-level code using our Ethereum decompiler.
- Annotate the analysis results to better understand what the compiled contract or dApp is doing.
- Automate or script your reverse engineering tasks via our API.
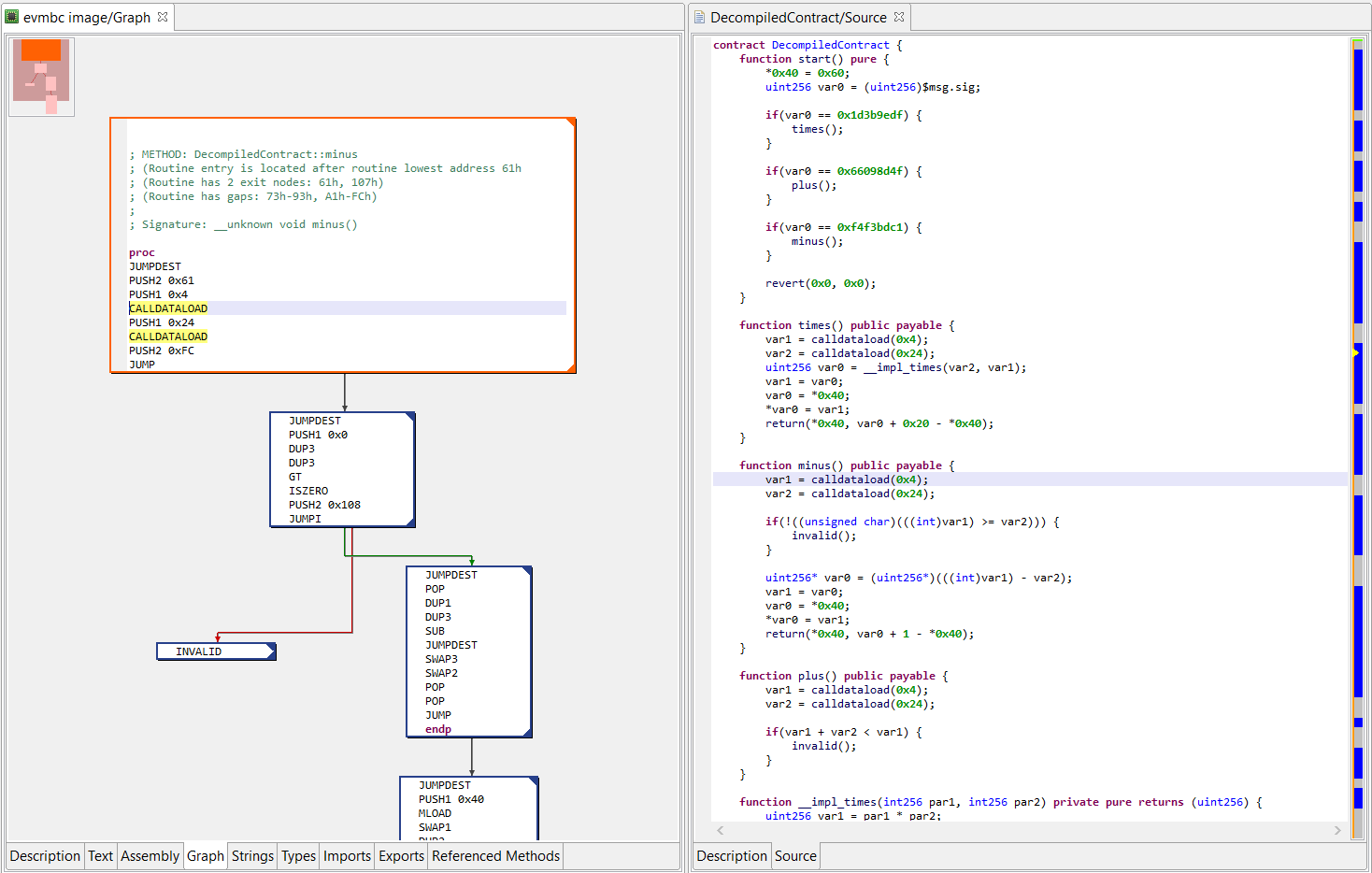
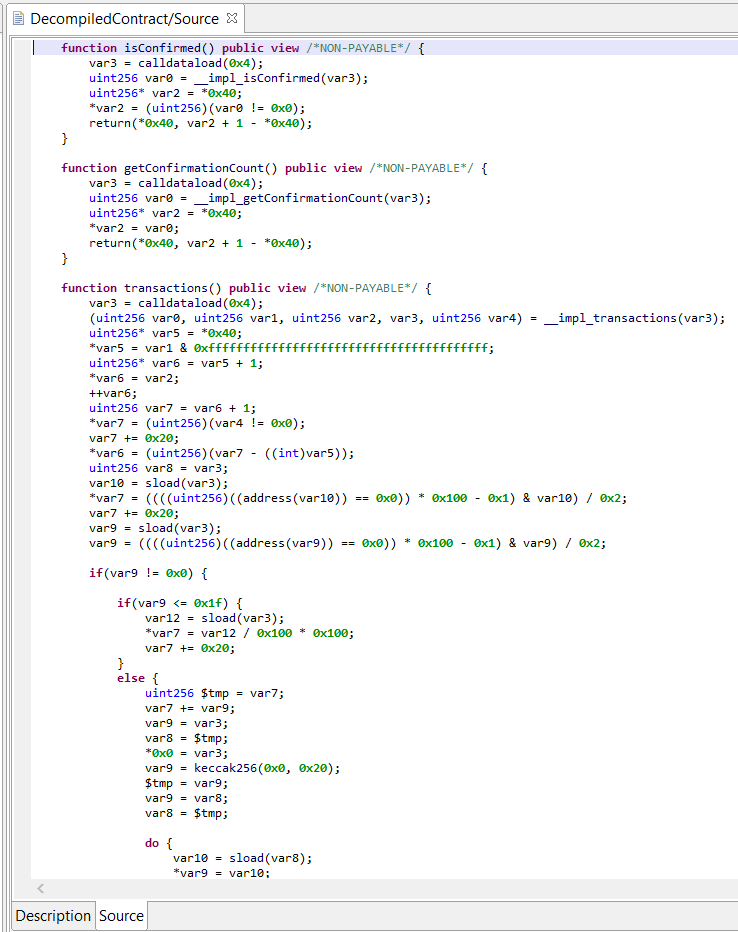
Example: See a decompiled output of the geneScience contract used by the popular CryptoKitties dApp.
The picture on the right-side shows JEB dual-pane "EVM assembly/decompiled code" view of a contract live on Ethereum's mainnet. (Click to enlarge.)
Decompiler Features & Capabilities
The decompiler modules provide the following specific capabilities:
- The decompiler takes compiled smart contract EVM code as input, and decompiles them to Solidity-like source code.
- The initial EVM code analysis passes determine contract's public and private methods, including implementations of public methods synthetically generated by compilers.
- Code analysis attempts to determine method and event names and prototypes, without access to an ABI.
- The decompiler also attempts to recover various high-level constructs, including:
- Implementations of well-known interfaces, such as ERC20 for standard tokens, ERC721 for non-fungible tokens, MultiSigWallet contracts, etc.
- Storage variables and types
- High-level Solidity artifacts and idioms, including:
- Function mutability attributes
- Function payability state
- Event emission, including event name
- Invocations of address.send() or address.transfer()
- Precompiled contracts invocations
On top of the above, the JEB back-end and client platform provide the following standard functionality:
- The decompiler uses JEB's optimizations pipeline to produce high-level clean code.
- It uses JEB code analysis core features, and therefore permits: code refactoring (eg, consistently renaming methods or fields), commenting and annotating, navigating (eg, cross references), typing, graphing, etc.
- Users have access to the intermediate-level IR representation as well as high-level AST representations though the JEB API.
- More generally, the API allows power-users to write extensions, ranging from simple scripts in Python to complex plugins in Java.
Our Ethereum modules were tested on thousands of smart contracts active on Ethereum mainnet and testnets.